
Labor variance is an accounting measure used to analyze cost rates and efficiencies connected with the compensation expense of employing staff. It’s most often used in manufacturing, where it’s referred to as direct labor variance and most frequently calculated using the staff directly responsible for turning raw materials into finished goods. The company A manufacture shirt, the standard cost shows that one unit of production requires 2 hours of direct labor at $5 per hour. Even with a higher direct labor cost per hour, our total direct labor cost went down!
Process of Labor Rate Variance Calculation
How would this unforeseen pay cutaffect United’s direct labor rate variance? Thedirect labor rate variance would likely be favorable, perhapstotaling close to $620,000,000, depending on how much of thesesavings management anticipated when the budget was firstestablished. Beyond the income statement, labor variances also affect the balance sheet. For instance, unfavorable variances can lead to higher accounts payable if additional labor costs are incurred but not yet paid. This can strain cash flow and liquidity, making it more challenging for the company to meet its short-term obligations.
Get Your Questions Answered and Book a Free Call if Necessary
An overview of these two types of labor efficiency variance is given below. Mary’s new hire isn’t doing as well as expected, but what if the opposite had happened? What if adding Jake to the team has speeded up the production process and now it was only taking .4 hours to produce a pair of shoes?
Direct Labor Time Variance
The flexible budget is comparedto actual costs, and the difference is shown in the form of twovariances. It is defined as the differencebetween the actual number of direct labor hours worked and budgeteddirect labor hours that should have been worked based on thestandards. Fluctuations in demand, changes in labor laws, and economic downturns can all affect labor costs. For instance, during periods of high demand, companies may need to pay overtime or hire temporary workers at higher rates, leading to unfavorable labor rate variances. Conversely, economic downturns might result in layoffs or reduced hours, impacting labor efficiency. Staying attuned to market trends and economic indicators can help companies anticipate and adapt to these changes.
What are the benefits of calculating direct labor yield variance?
In this case, the actual rate per hour is \(\$9.50\), the standard rate per hour is \(\$8.00\), and the actual hours worked per box are \(0.10\) hours. Next, labor efficiency variance is calculated by subtracting the actual hours worked from the standard hours allowed for the actual output, then multiplying by the standard labor rate. Suppose the standard hours for producing 500 units these tax credits could boost refunds for low are 800 hours, but the actual hours worked are 900. With a standard labor rate of $20 per hour, the labor efficiency variance would be (800 – 900) x $20, equating to a $2,000 unfavorable variance. This suggests inefficiencies in the production process, possibly due to inadequate training or outdated equipment. Standard costs are used to establish theflexible budget for direct labor.
Direct Labor Variances
Tools like Tableau or Power BI can be instrumental in visualizing these variances, making it easier for managers to identify patterns and take corrective actions. Effective leadership can optimize labor performance by setting clear expectations, providing timely feedback, and fostering a positive work environment. Poor management, on the other hand, can lead to miscommunication, low morale, and inefficiencies, all of which contribute to labor variance. Implementing robust management practices and leadership training programs can therefore play a crucial role in minimizing labor variances.
Direct Labor Mix Variance can be used to make a product more cost-efficient, less wasteful of resources, and save time during production. It is used to increase the profits of the company by saving money on labor costs. Jerry (president and owner), Tom (sales manager), Lynn(production manager), and Michelle (treasurer and controller) wereat the meeting described at the opening of this chapter. Michellewas asked to find out why direct labor and direct materials costswere higher than budgeted, even after factoring in the 5 percentincrease in sales over the initial budget. Lynn was surprised tolearn that direct labor and direct materials costs were so high,particularly since actual materials used and actual direct laborhours worked were below budget. Note that both approaches—the direct labor efficiency variancecalculation and the alternative calculation—yield the sameresult.
- As mentioned earlier, the cause of one variance might influenceanother variance.
- Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
- Implementing robust management practices and leadership training programs can therefore play a crucial role in minimizing labor variances.
- Thedirect labor rate variance would likely be favorable, perhapstotaling close to $620,000,000, depending on how much of thesesavings management anticipated when the budget was firstestablished.
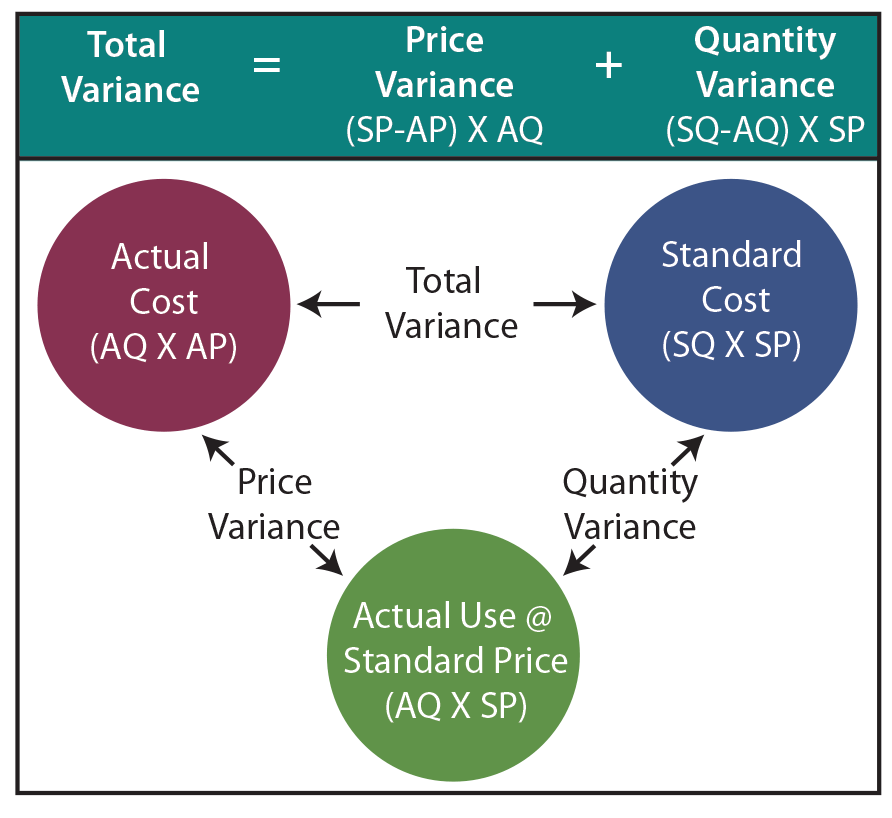
- By showing the total direct labor variance as the sum of the two components, management can better analyze the two variances and enhance decision-making.
Direct Labor Mix Variance is the difference between the budgeted labor mix and the actual labor mix used in production, which can lead to an over- or under-utilization of resources. Figure 10.7 contains some possible explanations for the laborrate variance (left panel) and labor efficiency variance (rightpanel). Another strategy involves continuous improvement initiatives such as Lean and Six Sigma. These methodologies focus on streamlining processes and eliminating waste, thereby improving labor efficiency. For example, Lean techniques can help identify bottlenecks in production that cause delays, while Six Sigma can provide a data-driven approach to reducing errors and rework.
Labor variance is shaped by a multitude of factors, each contributing to the complexity of managing labor costs effectively. Highly skilled employees tend to perform tasks more efficiently and with fewer errors, leading to favorable labor variances. Conversely, a less experienced workforce may require more time and supervision, resulting in unfavorable variances. Investing in continuous training and development can help mitigate these discrepancies by enhancing employee competencies. Favorable when the actual labor cost per hour is lower than standard rate. On the other hand, unfavorable mean the actual labor cost is higher than expected.
Labor variance has a direct and often profound impact on a company’s financial statements, influencing both the income statement and the balance sheet. When labor costs deviate from the standards set during budgeting, these variances are reflected in the cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement. Unfavorable labor variances increase COGS, thereby reducing gross profit and, ultimately, net income. This can signal inefficiencies to stakeholders and may affect investor confidence. United Airlines asked abankruptcy court to allow a one-time 4 percent pay cut for pilots,flight attendants, mechanics, flight controllers, and ticketagents. The pay cut was proposed to last as long as the companyremained in bankruptcy and was expected to provide savings ofapproximately $620,000,000.
The time it takes to make a pair of shoes has gone from .5 to .6 hours. Mary hopes it will better as the team works together, but right now, she needs to reevaluate her labor budget and get the information to her boss. Direct Labor Mix Variance is typically calculated by subtracting the actual amount of labor used from the budgeted amount, then dividing the result by the budgeted amount. To calculate Direct Labor Mix Variance you must first identify the exact amount of labor it requires to produce a product. Organizations can use DLYV to identify cost-saving opportunities, measure the productivity of their labor force, and improve operational efficiency. The most common cause of Direct Labor Mix Variance is a change in the staffing requirements for a particular job, such as the introduction of a new type of worker or skill.